

The week's shopping has turned out lavishly, there are leftovers after a festive dinner or you want to dispose of as little as possible before going on holiday?
Good thing that many foods can be frozen. The freezer extends the shelf life of fresh food by many weeks, sometimes months. To do this safely, it is worth paying attention to a few factors. How best to bring frozen food to icy temperatures, which containers are suitable and whether you should refreeze thawed food are questions that need to be answered.
Freeze food and extend the shelf life by many weeks and months in no time at all: Cooling fresh produce down to minus 18 °C in the freezer compartment is a clever move for optimum storage. This means you can enjoy seasonal products such as fresh asparagus even in winter and always have cooked dishes in stock.

Having a freezer compartment in the house can also save you from having to dispose of food. If you have bought too much or can't manage to use up all your supplies before your holiday, simply put them in the freezer or deep freeze. This is possible with countless products such as fresh fruit, vegetables, meat and fish as well as cooked dishes. The food trend 'meal prepping' - i.e. preparing meals in advance - saves a lot of time in stressful everyday life: Because if you cook ahead and freeze food in portions, you'll have a delicious dinner on the table in no time at all. Use the practical accessories from BORA for freezing and further processing.
Good to know: Food is usually frozen at a temperature of minus 18 °C. Germs and bacteria stop multiplying. This ensures significantly longer freshness.
From artichokes to courgettes: You can freeze a wide variety of foods. In general, the lower in fat and drier a product is, the more suitable it is for freezing in the cold. Fatty foods can also be brought to freezing temperature, but you should only store them in the freezer for a short time. Fatty minced meat, for example, will not keep for more than four weeks, even on ice. You can freeze cream for about three months.

Some foods are particularly suitable for further processing after defrosting as their consistency changes. This applies to apples and onions, for example: They lose their firmness to the bite, but can still be used for frying and cooking. Water-containing foods such as tomatoes, cucumbers and lettuce are also only suitable for freezing to a limited extent. After defrosting, they become mushy and the flavour suffers.
Raw potatoes and eggs should not be put in the freezerat all. Once defrosted, the potatoes change their flavour and become sweet, the eggs can burst when frozen. Cream cheese and yoghurt do not belong in the freezer either.
The shelf life in the freezer varies depending on the type of food. Lean meat, for example, can be frozen for longer than sausage. These guide values provide orientation:
You can also find more information on how long certain products keep chilled and frozen in our food storage overview .
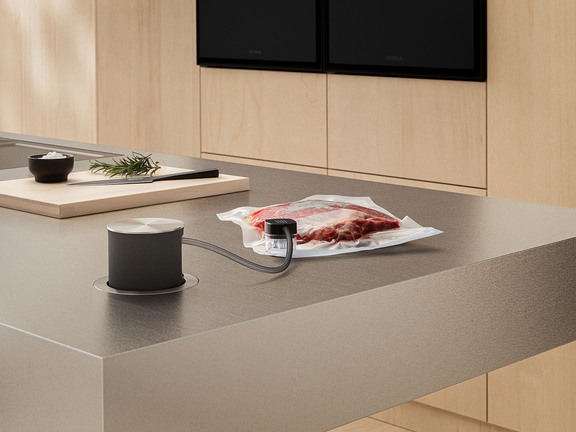

You can also freeze vacuum-packed food. This significantly extends the shelf life. Meat, for example, can then be stored for around twice as long. Vacuum packing also prevents freezer burncaused by the influence of air and preserves nutrients and vitamins for longer.
Once you have removed frozen food, you should process it quickly. This prevents germs from multiplying in the air. Some foods need to be defrosted completely before processing, others can be added directly to the pot or pan when frozen.

Tip: Depending on the quantity, it takes a few hours to defrost meat and co. Ideally, you should put the frozen products in the fridge the evening before.
Prepare your food ideally for freezing with one or two handles . To preserve quality and make it easier to take out:
Refreezing defrosted food is not usually a good idea. Germs and bacteria resume growth after defrosting. This can result in a high bacterial load. Meat and fish especially should be consumed soon after thawing and should not be refrozen. Exception: once cooked, they can be put back in the freezer.
Plastic, glass or stainless steel: you can freeze food in virtually any container. You merely need to ensure that it is frostproof and tightly sealed. Freezer bags should be sealed as airtight as possible.
To make it easier to take out, freeze bread in slices. Use an airtight container or freezer bag. This stops baked goods from drying out.
Practically all solid vegetable varieties can be frozen raw. These include cauliflower and broccoli, carrots, kohlrabi, mushrooms, peppers and many more. However, vegetables with a high water content can become mushy after thawing.
Conventional packaging often cannot withstand the temperatures in the freezer. It can become porous and it may release hazardous substances. It is best to transfer food to a separate container for freezing.
Freezer burn is not detrimental to your health. However, the flavour will be affected, meaning that food is generally no longer enjoyable.
As a rule, fruit and vegetables do not spoil in the freezer. However, after a long time in storage, they may lose flavour and nutrients and become mushy.